Soil is an important resource in agriculture. Conserving soil helps in maintaining its productivity.
Importance of soil conservation in agricultural environment
Soil conservation is carried out to keep the top soil in its place and preserve it for long term productivity.
Why should we conserve soil in the environment?
Activity 1
Finding out the importance of conserving soil in the environment.
Summary Points
Soil conservation helps to increase agricultural production. This promotes food security.
Methods of soil conservation in agricultural environment
We need to conserve soil in order to sustain its agricultural productivity. This can be done through various ways.
How can we conserve soil in the environment?
Activity 2
Searching and sharing information on methods of soil conservation.
Summary Points
Methods of soil conservation include the following:
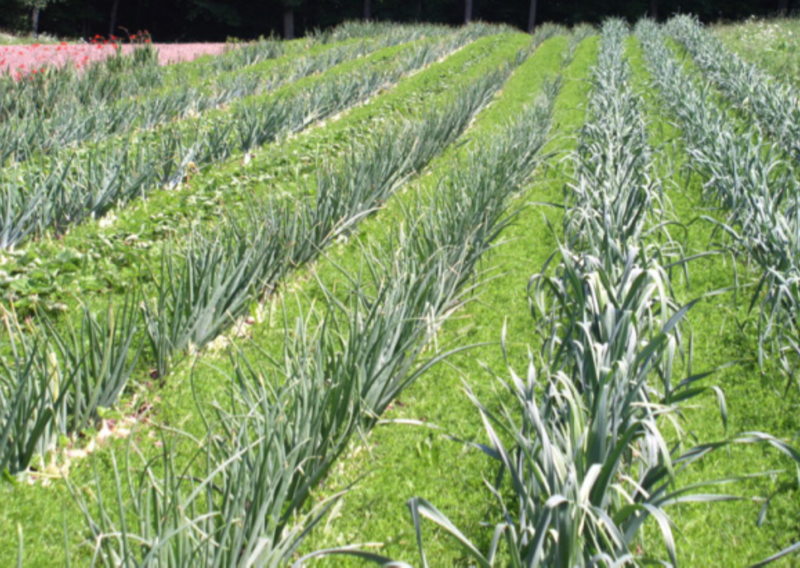
- Strip cropping – This is the growing of crops in such a way that crops, which give little soil cover such as maize are grown in alternative strips with crops having a good ground cover such as sweet potatoes. Strips of permanent vegetation such as grass can also be included. Strip cropping prevents loss of soil through surface runoff.
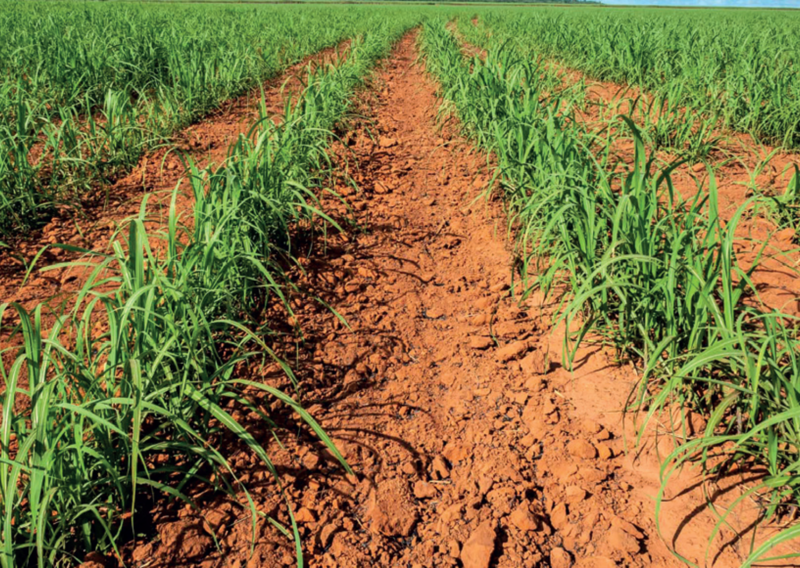
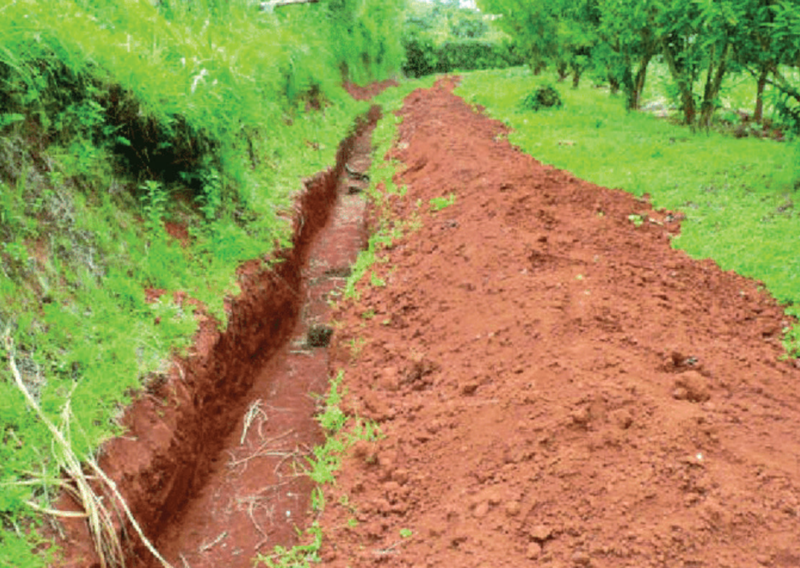
- Grassed waterways – These are natural or man‑made shallow channels through which excess rain water flows. Grass and other vegetation are planted or allowed to grow in the channels. Surface run off is directed into such water ways. The vegetation on the water ways lowers the speed of run off and traps eroded soil. Grassed water ways should not be used as track or grazing land. This would lead to loss of the vegetation that prevent erosion.
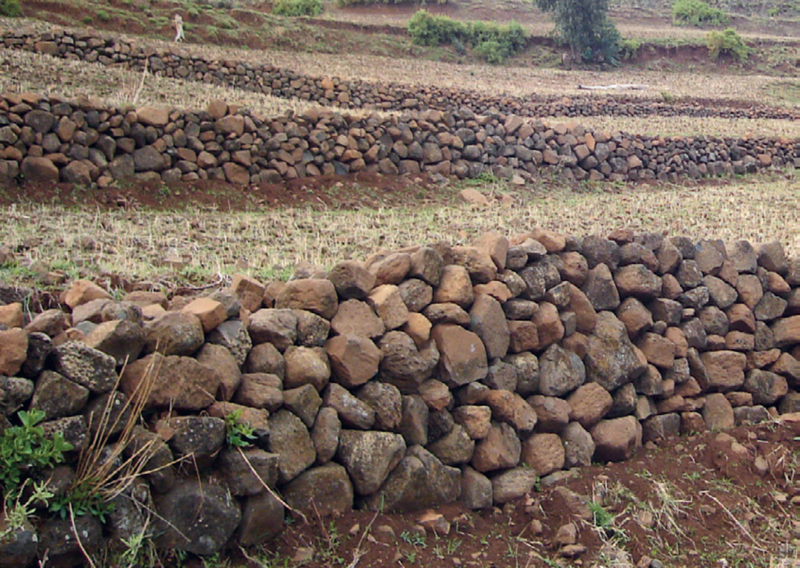
- Stone lines – These are stones arranged in the shape of a line along the contour to prevent the loss of soil down the slope through run off. The stones may be of different sizes. Stone lines impends the flow of surface runoff. This increases water infiltration especially in the semi‑arid areas. They are suitable for a gently sloppy land.
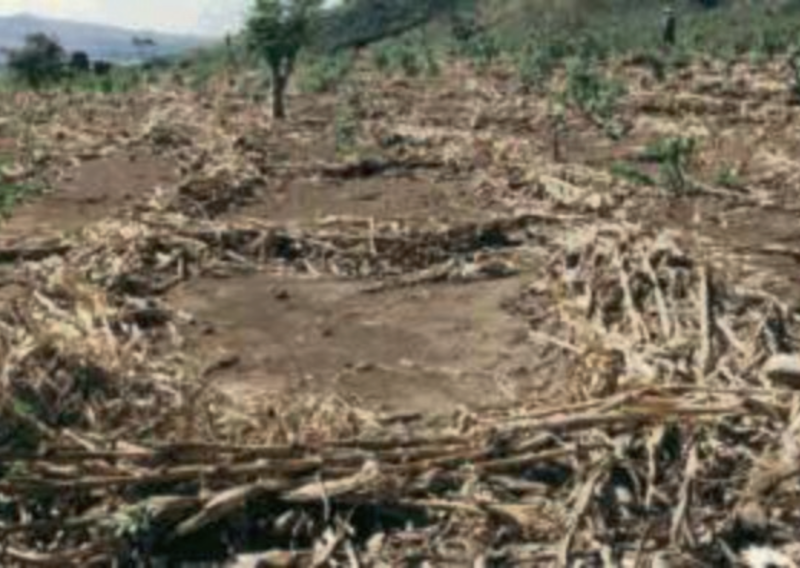
- Trash lines – These are plant materials or crop residues arranged along the contour in a cultivated field. They help to reduce speed of surface run‑off thus preventing loss of soil from the land. They also increase water infiltration into the soil. The trash lines should not be more than 1 m wide and 0.5 m high.
- Bund formation – A bund is a heap of compacted soil made along the contour. Grass may be planted on top of the bund to hold the soil together. Bunds help to reduce the volume of water flowing downward in a cultivated field after a downpour.
Practical Activity
How to conserve soil in the environment
We can develop skills in soil conservation by carrying out soil conservation activities in the school environment.
How can we conserve soil in the environment?
Activity 3
Carrying out soil conservation activities in the school environment.
Let us practise in school
Work in groups
- Identify a suitable site for carrying out the following soil conservation measures in the school environment:
- Strip cropping
- Grassed waterways
- Stone lines
- Trash line
- Bund formation
- Assemble the materials, tools and equipment required for carrying out the soil conservation measures selected.
- Carry out soil conservation measures using the steps given under each method of soil conservation as follows:
(a) Strip cropping
Steps:
- Select the crops to be planted.
- Plant the crops in alternate strips as illustrated in the photograph.
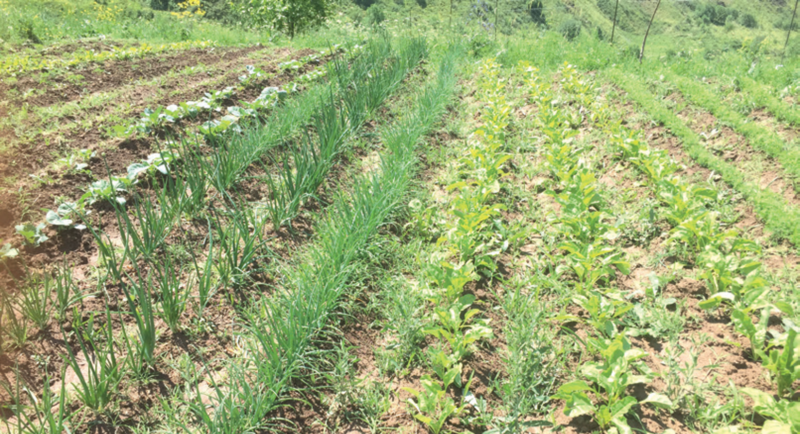

- Carry out crop management practices until the crop reaches maturity.
(b) Constructing grassed water ways
Steps:
- Select a ditch through which surface runoff flows during heavy rainfall.
- Plant grass along the ditch. Grass will slow the speed at which water moves and also prevent soil being eroded.
- Maintain the water‑way to attain effective results.
(c) Constructing trash lines
Steps:
- Establish contour lines at regular intervals with the help of the teacher as shown in the illustration.
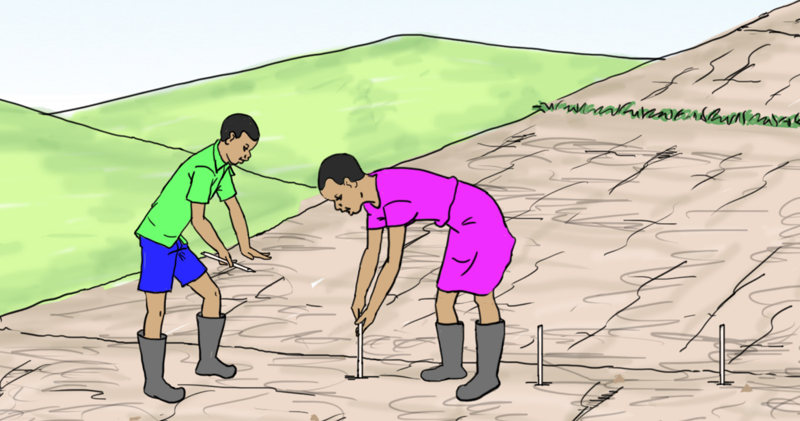
- Arrange the trash along the contour lines as shown in the illustration:
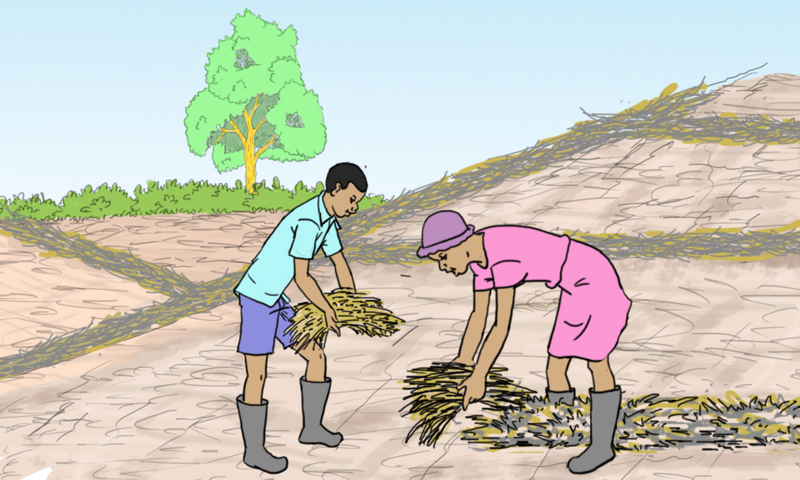

- Replace the trash every season after decomposition.

(d) Constructing stone lines
Steps:
- Select an appropriate site.
- Collect stones of various sizes and transport them to the site.
- Establish contour lines at regular intervals with the assistance of the teacher.
- Pile stones along a contour line with a width of around 35–40 cm and a height of around 25 cm.
- Place small stones upslope and the big ones downslope to slow down the run‑off, hold nutrient rich soil sediments and improve infiltration. The picture shows learners constructing stone lines.
- Keep the lines around 15–20 m apart depending with the slope.
- Regularly check and repair the stone lines in case of any damage from heavy rains.
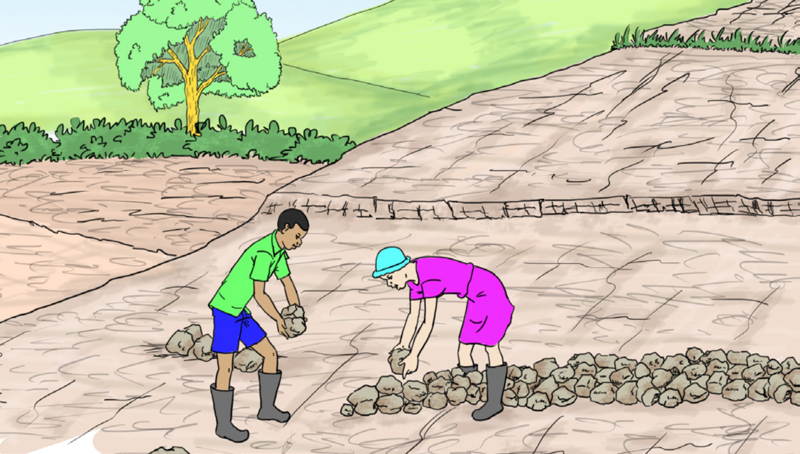

(e) Constructing bunds
Steps:
- Establish the contour lines and mark them using wooden pegs.
- Dig the soil from the upper side of the pegs and throw it on the lower side; as shown in the illustration.
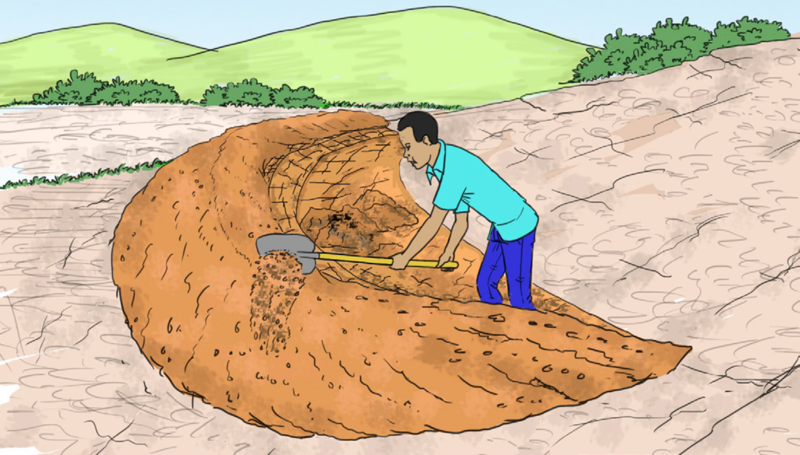

The heaped soil forms a bund along the contour line. The following photograph shows several bunds established along the contour lines.
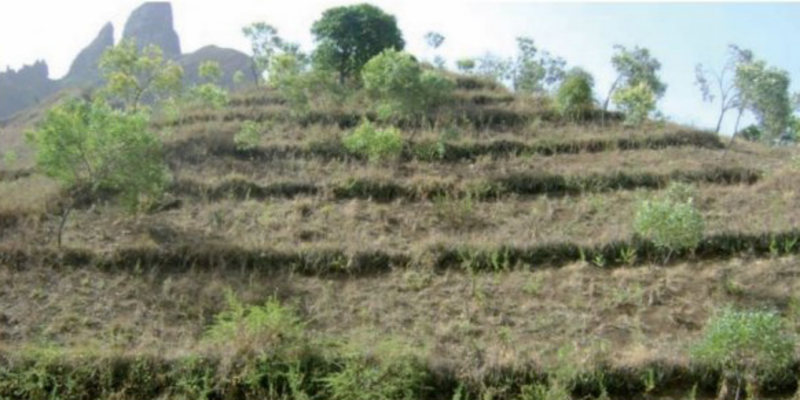

Discuss and share your experiences with others.
Summary Points
- Most of the soil conservation structures are constructed along the contour lines. Therefore, their construction starts with establishing the contour lines.
- Contour lines are established to guide on the position of the soil conservation measures.
A model of a farm layout
For maximum utilisation of the farm, we need to draw a farm plan which shows the various farm enterprises and where each one is placed. This plan is known as a farm layout.
How can we show various soil conservation measures on a model of a farm layout?
Activity 4
Constructing a model of a farm layout with various soil conservation measures.
Use the following picture as your guide for a layout of farm.
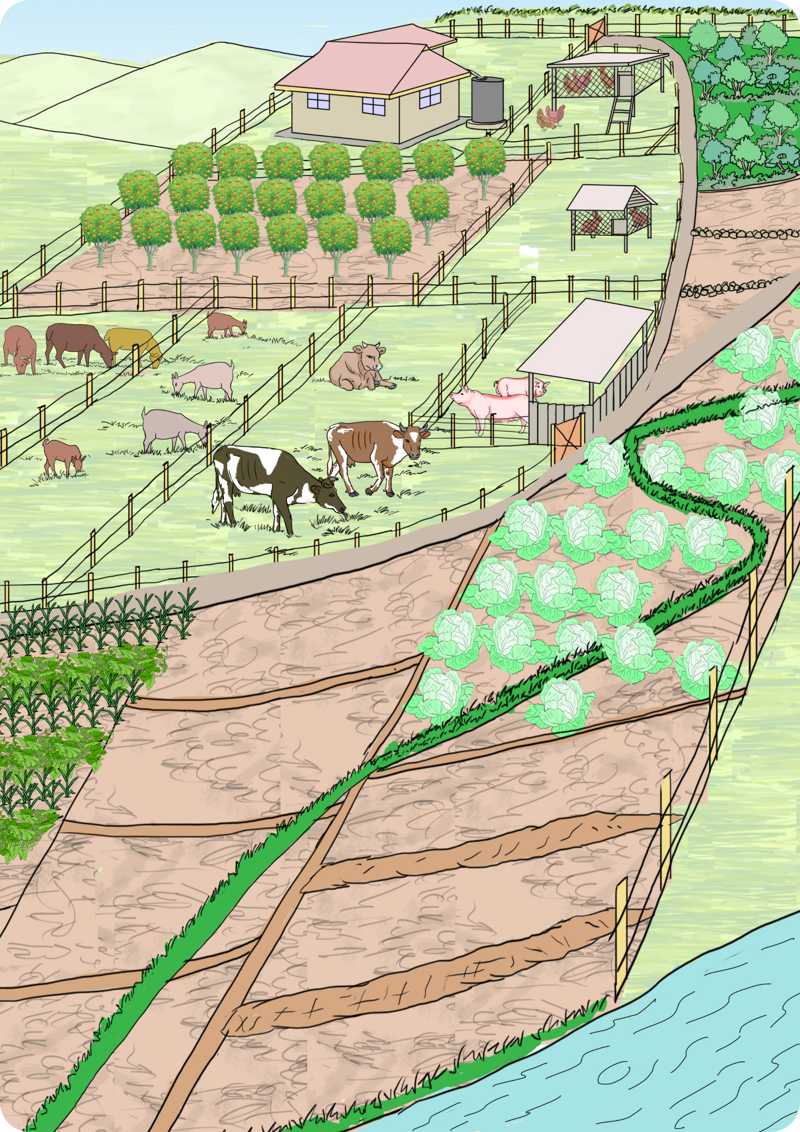
Let us practise
Work in groups
- Use digital devices and print media to search for information on how to draw a farm layout.
- Draw a layout of a farm using the following guidelines:
- Place the farm house near the road for easy transportation.
- Place animal houses away from the farm house to prevent unpleasant smell.
- Place crop fields where there is fertile soil.
- Place horticultural crops near water sources.
- Use the farm layout you have drawn to make a farm model from materials such as cartons, cardboards, soil and papier mache.
- Place various components of the farm layout and various soil conservation measures in your farm model.
- Clearly label each component and different soil conservation measures in your farm model.
- Exhibit the farm model in an open area of the school for the rest of the school community to learn from it.
Share your experiences with the school community.
Summary Points
- A farm layout is a plan of how various farm components (enterprises) are arranged and set up on a farm.
- A farm model guides the farmer to locate various farm activities and structures for convenience in a logical way.
- When planning to draw a farm layout, some of the factors to consider include the following:
- The size of the land: This will determine the number of enterprises to include.
- Topography of the area: This will determine the type of soil conservation measures to be used.
- The position of the road, rivers and other resources: This will help in determining where to place different farm structures.
- Security: For ease of supervision.
- Soil type: This will help to determine where to place the crops, the grazing land and the buildings.
- Government regulations: These are policies to guide crop enterprises and control the natural resources on the land, for example, cultivating along river bank, building too close to electric lines and roads.
- Climatic factors: This will be applied when selecting the type of enterprises to engage in.
- A papier mache is a strong molding material, which consists of waste paper mixed with glue.
Home project
Drawing a farm layout
A good farm layout ensures the land is well utilised for increased and sustainable agricultural production. The farm layout should not only show the arrangement of the various enterprises but also how the different soil conservation measures are placed.
Let us practise at home
Work with parents or guardians
- Walk around the farm at home and identify the various enterprises and their locations in the farm. Alternatively, you can do the same for a neighbouring farm.
- Draw a rough sketch of the farm layout and make suggestions on where different soil conservation, such as strip cropping, grassed waterways, stone lines, trash lines and bunds can be used to prevent loss of soil.
- Make a model farm layout of the farm at home, insert the various enterprises in their position on model.
- Show where the different soil conservation measures could be applied in the model.
- Write a report of your home project.
- Fill in the work card provided by the teacher.
- Share your experiences with the class.





