Listening and speaking
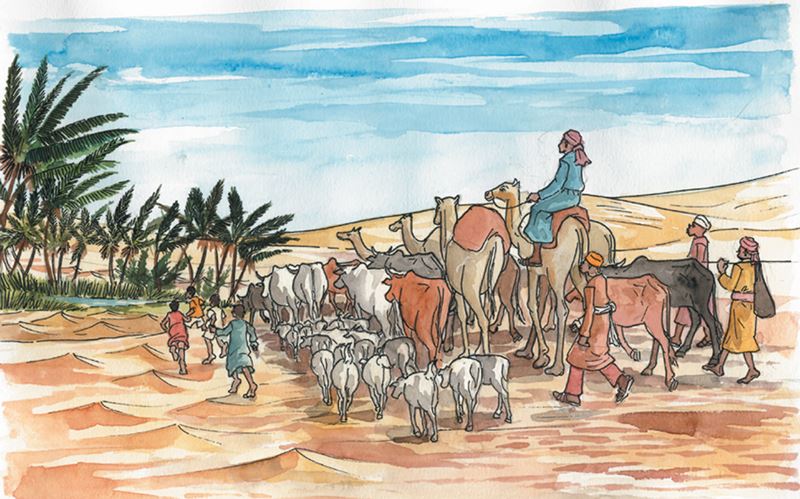

These people live in the desert. There is little vegetation but sand is everywhere. When winds blow, it becomes very uncomfortable. The people shield their faces from the dust that covers every place. Water is very scarce, and it is very hot during the day. Oases are few, but people are thankful all the same. Sometimes rains come, but when it is very hot, water evaporates before reaching the ground.
Discussion
- What are deserts?
- What kind of life do people who live in desert areas lead?
- What problems do you think nomadic people experience?
- What animals would you expect to find in arid areas?
Pronounce each of the following words correctly:
- city
- centre
- ceremony
- circus
- cent
- certificate
- citizen
- century
- cell
- cinema
- census
- celebrate
- circle
- cease
- certain
Note that the initial sound in each of the words is /s/. Although the words are spelt with letter c, the letter c is pronounced like the letter s.
This sound can also be found in the middle or at the end of a word.
Examples:
- innocent
- rice
- concentrate
- race
- deceive
- dance
- exercise
- price
- process
- advice
- nice
Read the following sentences aloud:
- You can visit the circus in the city centre.
- The innocent boy received a prize.
- The pupils celebrated when they received their certificates.
- The audience concentrated on the play.
- They are showing a funny film in a certain cinema.
- cite – site
Examples:
Preachers cite Bible passages frequently.
The school has moved to a new site. - cell – sell
- cent – sent
- cease – seize
Reading: Life in deserts
Deserts cover about one fifth of the surface of the earth. They are found in places where rainfall is very scarce. Although there are both hot and cold deserts, Africa’s deserts like the Sahara and the Kalahari are hot. There is little or no water in these places and few plants or animals can survive there. The most common sight in deserts is sand which is seen everywhere and a few people with their camels constantly looking for water. People in such places lead a nomadic life. They do little cultivation, except in places like Egypt where there is irrigation. This is possible because the longest river in the world, the Nile, passes through Egypt before joining the Mediterranean Sea.
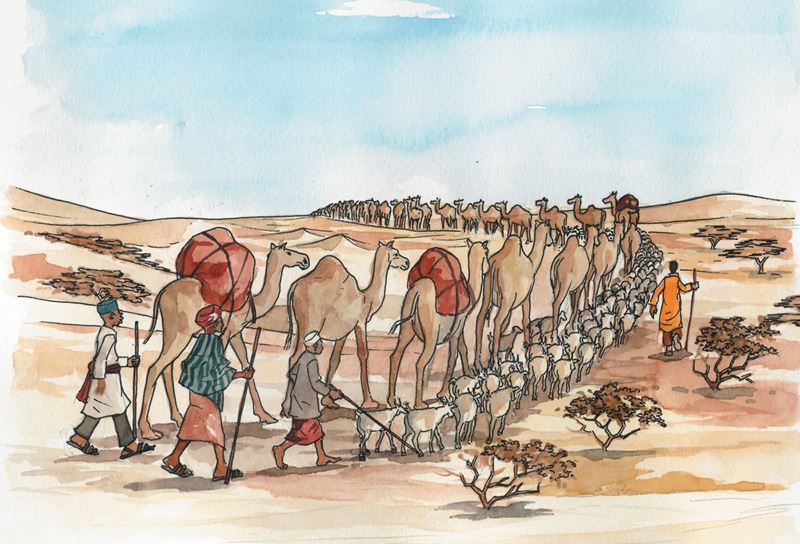
Slightly more than two thirds of Kenya’s surface is arid or semi-arid. The entire North Eastern Province, and parts of Rift Valley, Eastern and Coast Provinces receive very little rainfall. These regions are sometimes referred to as semi-deserts. Temperatures are very high during the day and very cold during the nights. The cool nights help both plants and animals by reducing moisture loss from sweating or breathing. The soil can range from sandy and fine-textured to loose rock fragments, gravel or sand.
In the arid and semi-arid parts of Kenya, most people are pastoralists. They move from place to place with their camels, herds of cattle and flocks of sheep and goats. They build temporary homes like manyattas because they do not stay long in one place. In a few places, you can find oases where the people get water for themselves and their animals. Wells and boreholes also exist. In such places, you will find a high concentration of people and livestock. Irrigation projects have been initiated along the Tana River in Garissa and Tana River districts.
In most deserts and semi-deserts, vegetation is sparse. Since the climate is dry, plants are mainly ground-hugging shrubs and short woody trees. Acacia and cacti are examples of such trees. They are drought resistant and have water-conserving characteristics.
There are few large mammals in deserts. This is because most of them are not capable of storing sufficient water and bearing the heat. Deserts also provide little shelter for large animals. The camel is the largest animal in arid areas. It survives because it stores water in its hump. It is a highly valued animal. The most common animals are small creatures which are able to dig holes in the sand where they hide during the day. There are also insects, reptiles and birds. Many of them are not active during the day. They come out at night when the desert is cooler. People have to watch out so as not to be bitten by some of these creatures. Scorpion bites, for example, are very painful.
Travelling in the desert is very difficult. Very few roads are tarred and ordinary cars are therefore unsuitable. Those who can afford use four-wheel-drive vehicles which are specially designed for rough places. A majority of the people, however, ride on lorries and trucks. Although life is difficult in arid areas, people are still able to make a living through hard work.
Exercise 2
Answer the following questions:
Discussion
What can be done to prevent the spread of deserts?
Build your word power
A. Match each of the following words with its meaning.
Word | Meaning |
tarmacked | |
very little | |
very short and near the ground | |
able to store water for long periods | |
land that is so dry that few plants can grow on it | |
started |
B. Use the words you have just learnt in (a) to make sentences.
- initiated
The community has initiated an irrigation project. - arid
- sparse
- ground-hugging
- tarred
- water-conserving
