In Environmental Activities, you learnt about the environment, different aspects of the environment, and how to care for it. Conserving our environment involves taking care of the things around us by protecting and managing them properly.
Soil conservation
In Grade 4, you learnt about conserving the environment by looking at the uses of soil and water in farming. In Grade 5, you will still learn about conserving the environment by looking at soil conservation through soil recovery, and water conservation through farming practices. Conservation of soil and water means using them in a way that they will still be available for use in future.
Soil erosion
When the topsoil is carried away, it exposes the ground underneath. Washing away of soil on land surfaces that is not covered destroys the land.
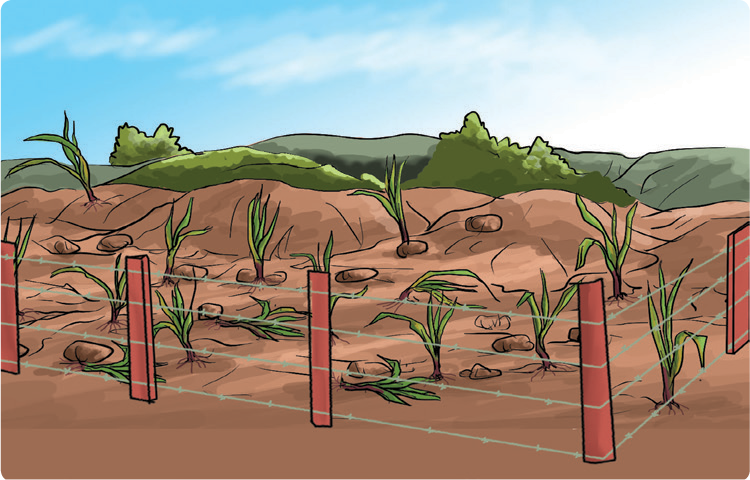
Let us think
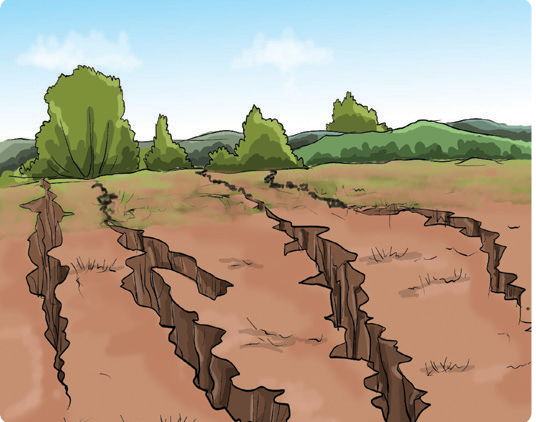
What happens to bare land when it rains heavily?
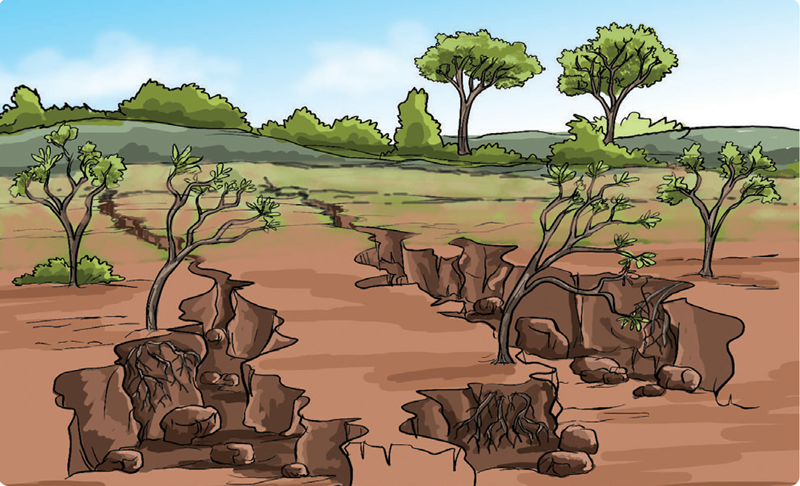

- What do you think caused the washing away of soil on the piece of land, to expose tree roots and form gullies in the picture?
- How much vegetation cover do you see in the picture?
- Can crops grow well on such land? Why?
Activity 2: Soil erosion on farming lands
In this activity, you will learn how soil erosion destroys the farm, leaving it unsuitable for crops.
Look at the pictures below and answer the questions that follow.
- Where have you seen such pieces of land?
- What do you think made the pieces of land that way? Discuss.
- What do you understand by the term 'soil erosion'?
- Growing crops on a piece of land
- The process during which top soil becomes more fertile
- The removal of top soil on a land surface
- Move around the school compound and the neighbourhood.
- Identify sites within the school and its neighbourhood that are eroded. List down the sites you have identified.
- Go back to school and discuss what happened to the soil in the sites you identified. Take notes in groups and make a group presentation in class.
- Connect to the internet.
- Click on YouTube.
- Search and watch video clips on 'soil erosion and its causes'.
- From the video clips, write down the meaning of soil erosion, and its causes. Share your findings in class.
Learning point
The removal of top soil on a land surface is called soil erosion. Some of the causes of soil erosion are surface runoff, wind, and destructive human activities on the environment.
Soil deposition sites
Let us think
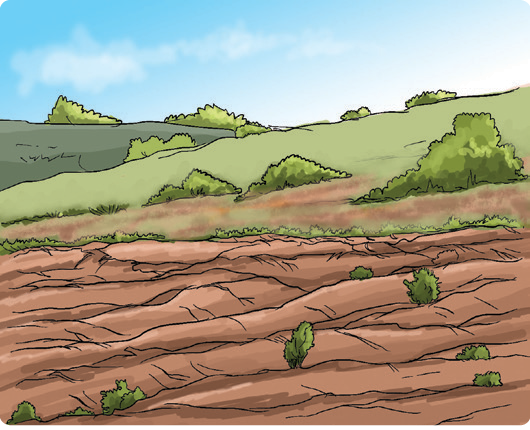
Where does soil carried by surface runoff end up within the environment?

- Why do you think the river is getting narrow while the riverbank is increasing?
- Humans have changed the shape of the river
- Soil is being deposited on the riverbanks
- The water level is rising
- What is soil deposition, as shown in the picture?
- Movement of eroded soil by water or wind onto a land surface
- Movement of eroded soil deep underground
- Where else have you seen soil being deposited along the riverbank, as shown in the picture?
- Move around your school compound or a farm in your neighbourhood.
- Identify parts of the land where soil has been deposited. Write down the parts you have identified.
- Go back to school and discuss in groups how soil was deposited in the area identified. Take notes and make a class presentation of your findings.
Learning point
Soil deposition is the placing of eroded soil by water or wind on a land surface. Soil is deposited in places such as ditches and low-lying areas that hold surface runoff of the land.
Soil recovery
Let us think
How can deposited soil be recovered?
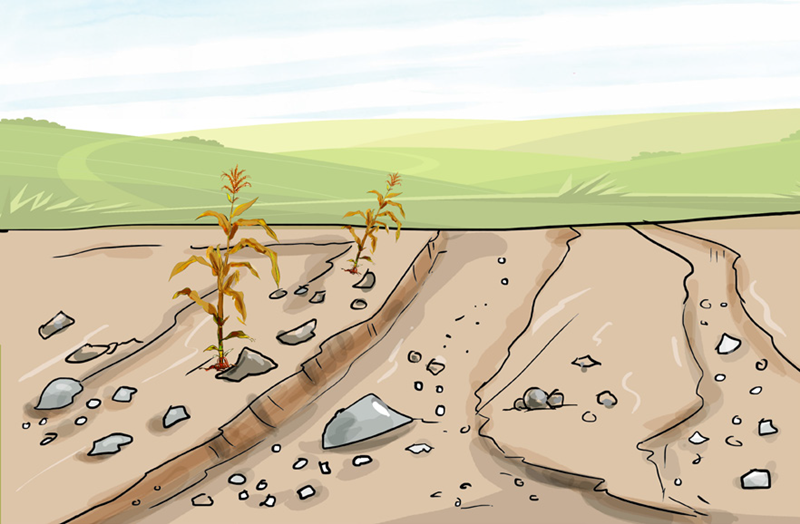
- Where did the soil that was eroded on the land shown in the picture above go to?
- The soil evaporated into the air.
- The soil was washed away by surface runoff.
- The soil was washed away deep underground.
- How can the eroded soil from the land be collected back?
Discuss and present your ideas in class.
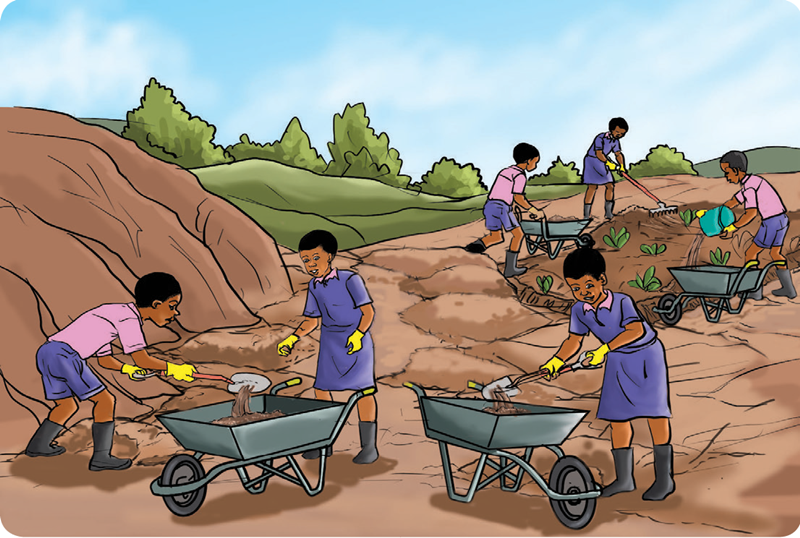

- What are the learners in the picture doing?
- Collecting deposited soil
- Collecting plants
- Which tools and equipment are the learners using?
- Hoe
- Wheelbarrow
- Gumboots
- Gloves
- Shovel
- Spade
- Rake
- Buckets
- What do we call the activity the learners are engaging in?
- Soil deposition
- Soil erosion
- Soil recovery
- What safety precautions should the learners observe?
- What is soil recovery?
- Collection of deposited soil from deposition sites
- Improvement of soil fertility
- Digging holes in soil to plant crops
Learning point
Soil recovery is the collection of deposited soil from deposition sites.
Recovered soil can be used for farming.
Importance of recovered soil
Let us think
How can soil deposited elsewhere be made useful again for farming?
A
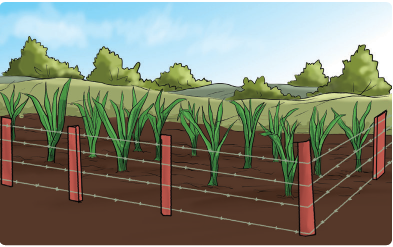
B
Compare picture A and B.
- Which plants grow on recovered soil? Give reasons.
- Which plants grow on eroded soil? Give reasons.
Activity 9: Collection and use of recovered soil
In this activity, you will recover eroded soil and use it for farming.
What you need: containers, spades, fork jembe, jembe, garden trowel, watering can, garden line, tape measure, seeds or seedlings, and gloves.
What to do
- Collect soil from soil deposition sites and place it in containers.
- Carry the soil to the school garden and select two eroded sites.
- Spread the soil on one eroded site as shown in the picture and leave the other eroded site as it is.
- Plant seeds or seedlings of your choice on the two sites.
- Observe and keep records, such as the height of the crops in both sites after sometime.
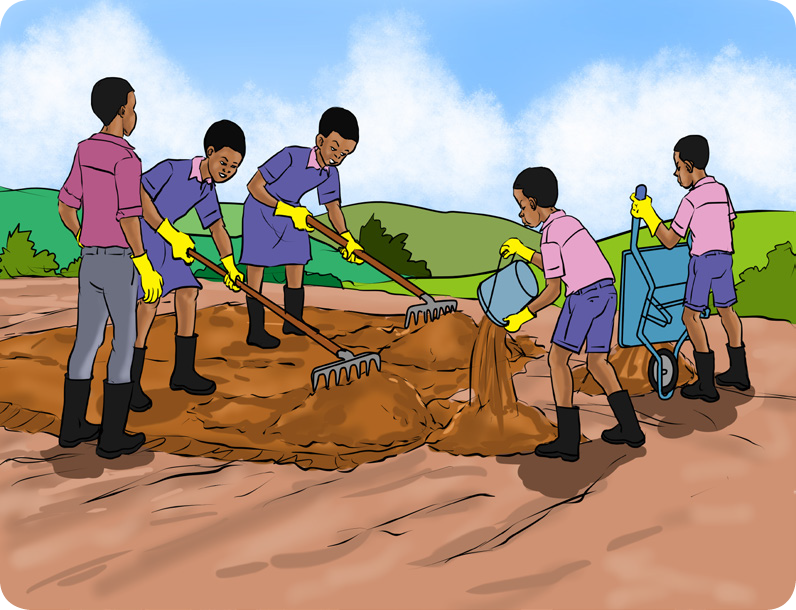

- Which seeds or seedlings did you choose to plant? Why?
- Which site is more likely to produce healthy-looking plants? Why?
- What differences do you expect between the crops in the two sites?
- What is the importance of recovering deposited soil? Discuss.
- What safety precautions did you observe when planting the crops?
Learning point
Recovered soil is more fertile than soil in an eroded site. The top soil in an eroded site has been removed, making the soil less fertile. Plants grow well in recovered soil because it is fertile.
Home activity
With the help of your parents or guardians, collect deposited soil from deposition sites at home or in the neighbourhood. Use the soil to grow crops at home.
Assessment 1
- What is soil erosion?
- The settling of eroded soil on certain land sites
- The removal of top soil from a land surface
- Collecting eroded soil for reuse in farming
- Mark the causes of soil erosion.
- surface runoff
- sun
- wind
- light rain
- destructive human activities
- soil recovery
- What is soil deposition?
- The settling of eroded soil on certain land sites
- The removal of top soil from a land surface
- Collecting eroded soil for reuse in farming
- What is soil recovery?
- The settling of eroded soil on certain land sites
- The removal of top soil from a land surface
- Collecting eroded soil for reuse in farming
- Why is recovered soil useful in farming?
- it is fertile
- it is infertile
- A farmer’s land is on a sloping area and has been seriously eroded. Suggest practices which the farmer can use to prevent further erosion of the soil.
- Give reasons why we need to conserve soil from soil erosion.
- All eroded soil is deposited on land. True or false?
- True
- False
- Match the statements correctly.
- The removal of top soil -
- The settling of eroded soil on certain land sites -
- Collecting eroded soil for reuse in farming -