Introduction
In modern society, computers play an important role in our day-to-day’s activities. It has become a common practice to find computer-based systems in banks, retail stores, government agencies, entertainment industry and media houses. To adapt to the ever changing technological world, one needs to be knowledgeable and a competent user of computers and portable devices such as mobile phones and tablets. In this chapter, we begin by defining the term computer then discuss its characteristics, applications, historical development and safe use.
Definition of a computer
A computer is an electronic device capable of receiving data (input) and performs a sequence of operations (processing) to produce output also known as information. To process data into desired information, a computer uses a set of instructions known as program also referred to as software. Figure 1.1 shows a diagram depicting how a computer program instructs the computer to accept data as input, and then process it to produce the desired output.
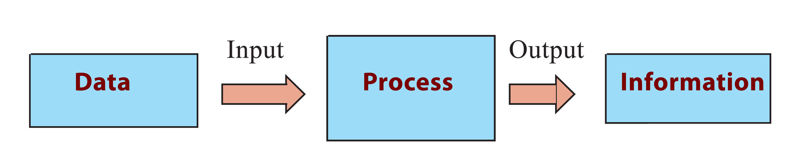
It is important to note that the term data is used in computing to refer to raw facts such as numbers, letters and symbols that have no meaning to the user. On the other hand, the term information is the processed data that is meaningful to the user.
Characteristics of a computer
Although computers do not have natural feelings and intelligence like human beings, the following are basic characteristics that makes them better:
- Fast: In terms of speed, a computer can perform calculations within seconds that human beings would take hours to complete
- Accurate: Unlike human beings who make errors, a computer has high degree of accuracy regardless of the complexity and number of times a calculation is performed.
- Versatile: Computers are flexible in that they can be used to carry out different types of activities such as typing, calculations, and playing music.
- Reliable: Computers are more reliable because they do not get tired or bored in processing repetitive tasks.
- Memory: Computers have in-built memory used to store and recall (retrieve) large amount of data compared to human memory recall.
- Diligent: A computer can perform repetitive or routine tasks without getting bored, tired, fatigued or losing concentration.
