The Position of Africa
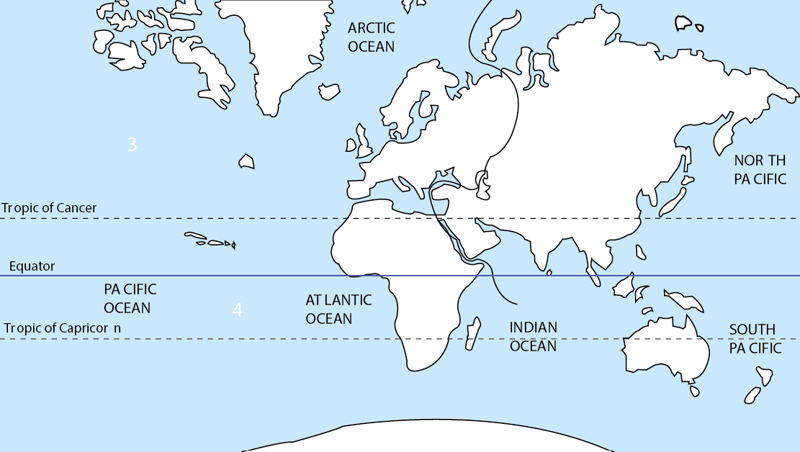
Africa is the second largest continent in the world, with an area of about 30.3 million km2. The largest continent is Asia and the smallest continent is Australia and New Zealand, as shown in Table 1.1. The position of Africa in relation to other continents of the world is shown in Figure 1.1 below;
Continent | Area |
1. Asia | 43 608 000 km2 |
2. Africa | 30 335 000 km2 |
3. North America | 25 349 000 km2 |
4. South America | 17 611 000 km2 |
5. Antarctica | 13 340 000 km2 |
6. Europe | 10 498 000 km2 |
7. Australia and New Zealand | 7 682 000 km2 |
- North
- East
- South
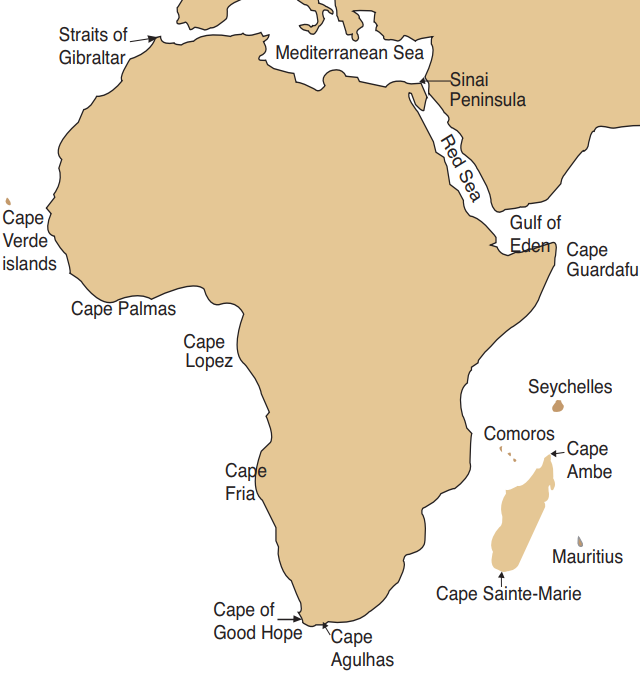
The African continent lies between latitudes 37°N, 35°S and longitudes 25°W, 58°E. Africa is almost an island since it is separated from other continents by water bodies apart from the Suez canal which cuts through the Sinai Peninsula. The water bodies that surround Africa are:
- Mediterranean Sea to the north.
- Red Sea to the North-East.
- Indian Ocean to the East.
- Atlantic Ocean to the West.
- Antarctic Ocean to the South.
The seven continents are surrounded by oceans and seas. Africa is held onto Asia by the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. A peninsula is a land that is almost surrounded by water. Africa is almost an island, as the Suez Canal cuts through the Sinai Peninsula. Africa is separated from the Iberian Peninsula in Europe by the 14.5 km wide Straits of Gibraltar and separated from the Arabian Peninsula in Asia by the Straits of Bab el Mandeb, to the east of Djibouti, as shown in Figure 1.3.
- Palmas
- Fria
- Suez
- Saldanha
- Winam
- Delagoa
- Ambe
- Agulhas
- Aqaba
- Guinea
- Lopez
- Sainte-Maria
- Table
- Guardafui
- Good Hope
- Gabes
- Alexander
- Aden
The Shape of Africa
The shape of Africa is not balanced. It is wide in the north and narrow towards the south. The Equator, which runs across Africa, nearly divides the continent into two equal parts. The furthest point in the north is Cape Bon in Tunisia at 37° North, which is 4 100 km from the equator. The furthest point in the south is Cape Agulhas in South Africa at 35° South, which is about 3 800 km from the equator.
This makes Africa be the only continent that is crossed by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. As we shall learn later, this has an effect on the climate experienced in Africa. The west-to-east distance on the landmass of Africa is about 7 200 km, which is from Cape Verde in Senegal to Cape Guardafui in Somalia. But the distance is greater when measured from Cape Verde Islands in the Atlantic Ocean at 25°W to Mauritius Islands in the Indian Ocean at 58°E, which is about 8 500 km.
A study of the edges of the landmass of Africa reveals that the coastline is not straight. In some sections, the land stretches outwards into the oceans to form capes and in some sections, the water has stretched into the land to form bays. The following are some capes and bays of Africa:
Bays | Country |
Delagoa | Mozambique |
Alexander | South Africa |
Walvis | Namibia |
Ungwana | Kenya |
Agulhas | South Africa |
Capes | Country |
Blanc | Western Sahara |
Guardafui | Somalia |
Agulhas | South Africa |
Lopez | Gabon |
Fria | Namibia |
Explore
Use your atlas to locate the capes and bays in Africa. Make a list of 10 capes and 10 bays in Africa.
The Size of Africa
We saw earlier that Africa is the second-largest continent in the world. Africa is about 20% of the world’s land surface with an area of 30 335 000 km2.
How many times is Africa larger than Europe and North America?