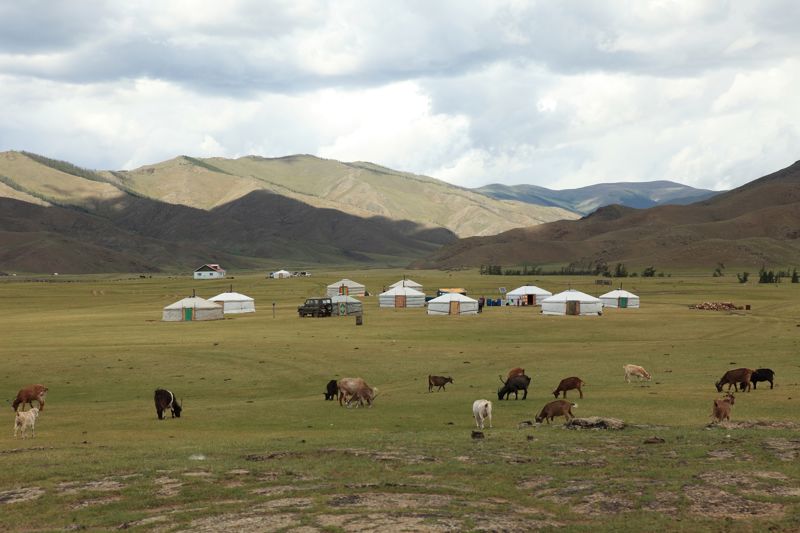
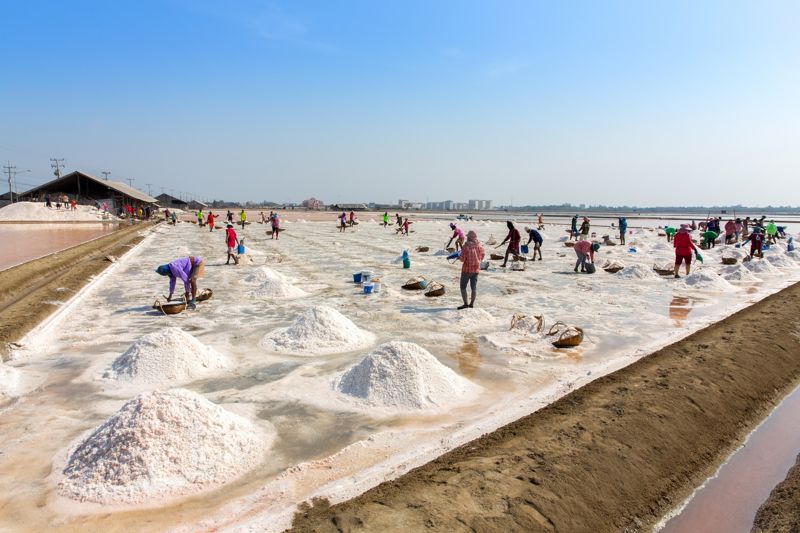
Plains cover a large part of the land. Their terrain is diversified by occasional uplands, single mountains and also some mountain ranges and valleys intersecting the ground. The appearance of the plain depends on the absolute height and formation, as well as on the rocks it consists of. Compared to the mountains, the plains are much more inhabited. Most of the world's population lives in the coastal lowlands because of the productive soils for farming and the favorable conditions for settlements.
The plains are located at different altitudes
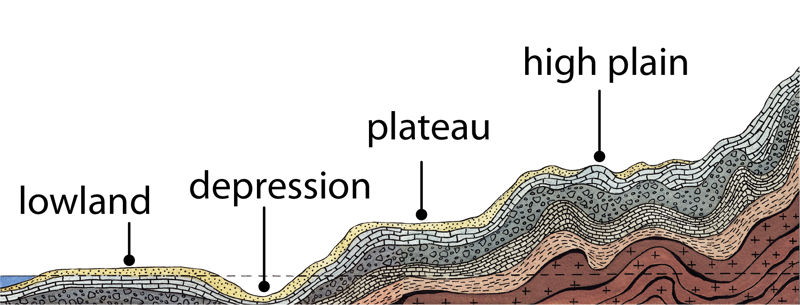
Flat areas with absolute altitudes below 200 m are called lowlands. They are mostly located along the coast or in the estuaries of large rivers, such as the Amazon, Mississippi, Indus-Ganges lowlands. Lowlands are mostly formed in areas where the ground sinks and where wind and water have, over time, carried sediment from higher areas.
Most of the lowlands have been formed by the subsidence of the earth's crust, which has resulted in flooding of the area and the accumulation of sediments at the bottom of the formed water bodies. Any region of the globe can sink and rise once during a very long geological history. Therefore, the bottom of a water body once filled with sediment may rise again later. Estonian topography has also developed in this way.
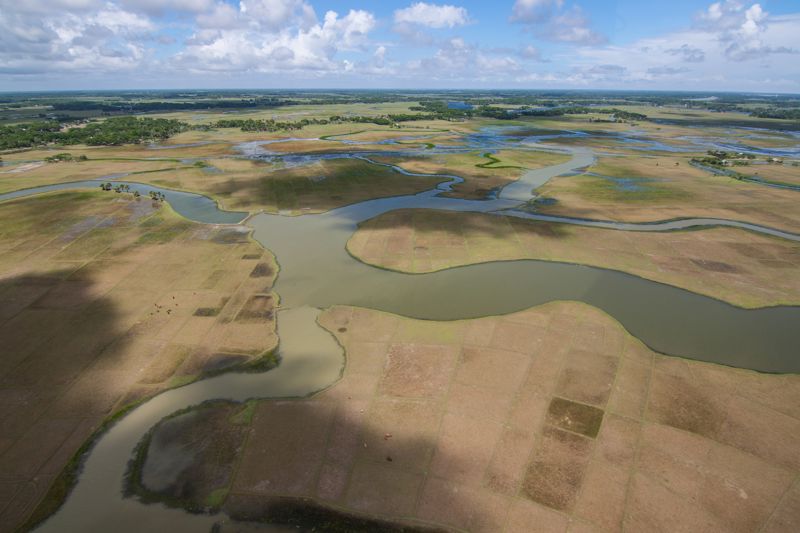

Extensive sediments have formed in the estuaries of high-flowing rivers, where the river is divided into several branches.
The limestone plateau and sandstone areas that formed in the sea hundreds of millions of years ago have, over time, risen above the level of the world's oceans, and there are various valleys, depressions and terraces on their surface. The lowlands of the Central Danube in Hungary, Austria, Slovakia, Romania and Serbia are part of the bottom of the former Thetis Ocean. Today, this lowland with a very flat surface is surrounded by the Alps and the Carpathians.
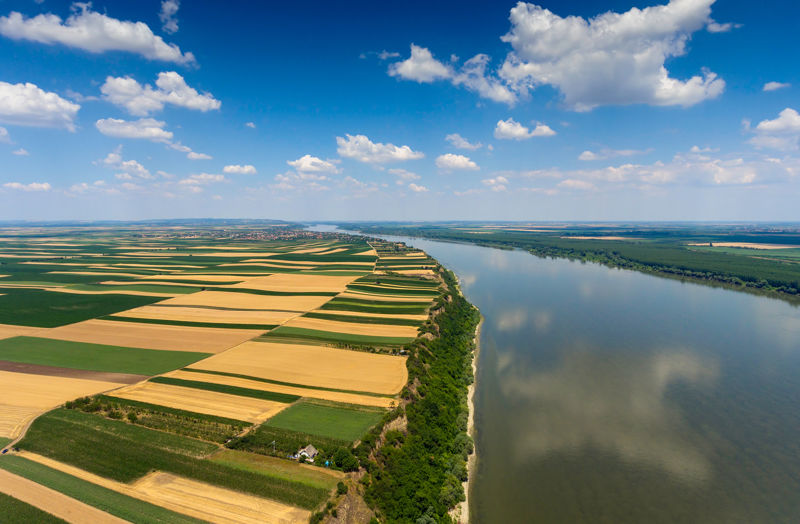

There are large areas in many parts of the world that are below sea level but are not flooded. These are called depressions. On the maps, the height of the depressions is indicated by a minus sign. For example, the Caspian Basin is up to 28 m below the world's sea level. However, the area around the Dead Sea in the Middle East is almost 400 m below sea level.
A plain can also form in places where the crust gradually rises or where a high area has worn down over a long period of time.
Only the valleys of rivers and the terraces split the flat surface of a plateau. They can also be found in Estonia, for example, the land of Harju and Viru, which is bordered in the North by Estonian limestone bank as a high step on the sea side.
The flat area rising several hundred meters above sea level is a remnant of the former mountains and highlands and is called high plain. For example, the Mexican capital Mexico City in Central America is located on a plain more than 2,000 m above sea level. The Sahara Desert in North Africa is located on a plain between 500 and 1000 m. It is part of a large high plains across the African continent, the only mountainous terrain of which has survived to this day.

Plateau is higher than the surroundings, an area that has been flat for a long time. It is formed by unfolded sedimentary rocks.



- Central Plains
- Altiplano
- Indus-Ganges Lowland
- Mississippi Lowland
- Amazon Lowland
- Colorado Plateau
- Mexican Plain
- Dead Sea Depression
- Caspian Depression
Human activities in lowland areas
Plain areas, especially lowlands, depressions and plateaus, are densely populated and have the most diversified economic activities on earth. The most densely populated areas are concentrated on the coasts of the seas and oceans. But there are also many cities inland, mainly by rivers and lakes.
It is much easier for people to live on the plains than in the mountains, because the climatic conditions are mostly more favorable there, there is more agricultural land, it is easier to build roads, rivers are mostly navigable, and so on.
How a person can manage in an area depends largely on nature. The tundra peoples hunt, fish and breed reindeer, in the forests there is a lot of forestry, but also agriculture. Grasslands have the most productive soils in the world for growing grains and many other crops. There are many sedimentary mineral resources on the plains, such as oil, natural gas, coal, salt.
Think
Would you prefer to live in a mountain or flat area? Why?
- The plains are well suited for both plant production and animal husbandry.
- Inland plains are the most densely populated.
- There is more land suitable for agriculture on the plains than in the mountains.
- The rivers of the plains are shallow and not easily navigable.
- The road network of the plains is denser than in the highlands.
- On the plains, mainly mineral resources stored in sedimentary rocks are procured.
- Forest management is easier on the plains than in the mountains
- The most fertile soils are in the tundra plains.
Definitions
- plain – an area with small elevations and low articulation
- lowland – flat land that is at, or not higher than 200 m above, sea level
- depression – a plain below sea level
- plateau – an area higher than the surroundings, which has been leveled over a long period of time
- high plain – a highland formed by the wear and tear of a mountain






