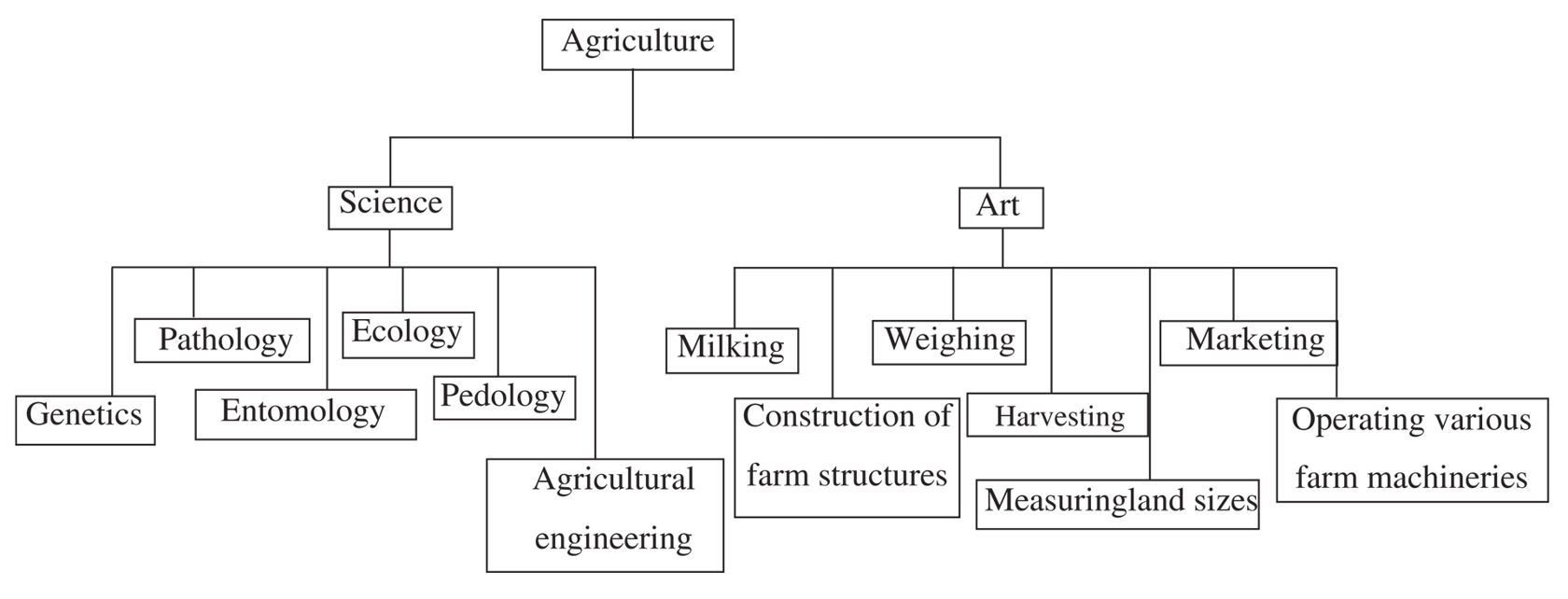
Agriculture can be defined as the science and art of crop and livestock production.
Agriculture can be regarded as an art as it involves the application of human skills which can be manipulated e.g. milking, construction of farm structures, measuring of land sizes, weighing, harvesting, marketing, operating farm machinery and cultivation.
On the other hand, it can be regarded as a science because of its application of intellectual and practical activities through observation, experimentation and analysis. This involves specialised areas e.g.
Genetics: This is the study of heredity and variation in organisms and is useful in the breeding of crops and animals.
Pathology: This is the branch of medicine concerned with the cause,symptoms and control of diseases.
Entomology: This is the branch of science concerned with the study of insects and their control.
Ecology: This is the study of the relationships between living organisms and their environment.
Pedology: This is the study of soils.
Agricultural engineering: This is the application of scientific principles to the design, construction, and maintenance of agricultural tools and machinery.